What is infertility?
Infertility is a pathological condition defined as the incapability of a sexually active couple to conceive within a year of non protected intercourses.
About 10-15% of all couples have a reduced ability to naturally procreate and studies estimate that 10% of males in reproductive age might be hypofertile, when it might be likely that in one case out of two the difficulties to obtain a natural pregnancy are related to males’ reproductive disorders.
INFERTILITY ≠ STERILITY
Even though “infertility” and “sterility” are often overlapping terms in collective imagination, there is a clear distinction between them. The latter indeed is defined as the impossibility to conceive, due to irreversible causes. Whereas infertility is a condition which causes might be solved.
Male infertility: Risk Factors
Idiopathic infertility: when no cause exists
Idiopathic infertility: defines a condition that occurs when all medical exams have been done and no specific cause could be found to explain the impossibility to conceive.
In this case, the therapeutical approach has to deal with seminal alteration. Once organic causes are excluded, after a careful anamnestic evaluation, the healthcare professional will evaluate the patient’s general conditions to identify the habits and lifestyle behaviors that might influence the quality of seminal fluid.
Major causes for male’s infertility
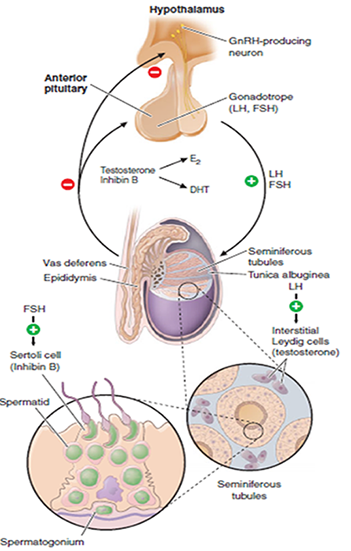
Among the hormonal causes, metabolic hypogonadism is fundamentally important and is considered one of the major causes of male infertility.
PCOS stands out as one of the most frequent hormonal causes of infertility.
The evaluation of the type of nutrition is fundamental, in fact it is now widely recognized that sedentary lifestyle, overweight, obesity, metabolic syndrome, poor diet and, above all, insulin resistance are important risk factors that reduce the probability of conception in both sexes, but especially in males. Therefore, by correcting these conditions through a targeted diet therapy, lifestyle changes and additionally the use of specific supplements, such as D-Chiroinositol, it is possible, eliminating the metabolic cause, to improve fertility and the reproductive situation of the patient.
Insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinemia prolonged over time, alters the hypothalamic release of GNRH and therefore of gonadotropins, leading to an increase in LH and a reduction in FSH. This condition, at a testicular level, reduces the proliferation of Sertoli cells and makes them less responsive to the action of testosterone, compromising spermatogenesis.
Furthermore, since fat is physiologically capable of converting male sex hormones into female hormones (estrogen), in conditions of overweight / obesity the patient can face an imbalance in the quantities of male sex hormones.
All of this will lead to an altered production, a reduced count and a reduced sperm motility, resulting in seminological conditions of oligo-astheno-teratospermia.
IMBALANCE IN LH / FSH RATIO
ALTERED SPERMATOGENESIS

INFERTILITY
DCI as an aid for fertility:
why?
1. Its role in the treatment of male infertility
The insulin sensitizing action of D-chiroinositol conjugated to an appropriate lifestyle modification, allows to reduce compensatory hyperinsulinemia, reduce fat allowing a restoration of the normal release of GNRH and gonadotropins (LH-FSH) reducing the excess of estrogen.
Furthermore, the DCI has shown to possess antioxidant and facilitating capacities on fundamental mitochondrial enzymes such as pyruvate dehydrogenase, leading to a better mitochondrial function also at the spermatozoon level.
The discovery that inositols have a positive effect on the glucose metabolism has broadened the horizons of the possible therapies, reducing the side effects and reaching the therapeutic objective at the same time.